The RBI projected inflation at 4.9 per cent in the April-June quarter and at 3.8 per cent for the September quarter.
The government has tasked the Reserve Bank to ensure inflation remains at 4 per cent, with a margin of 2 per cent on either side.
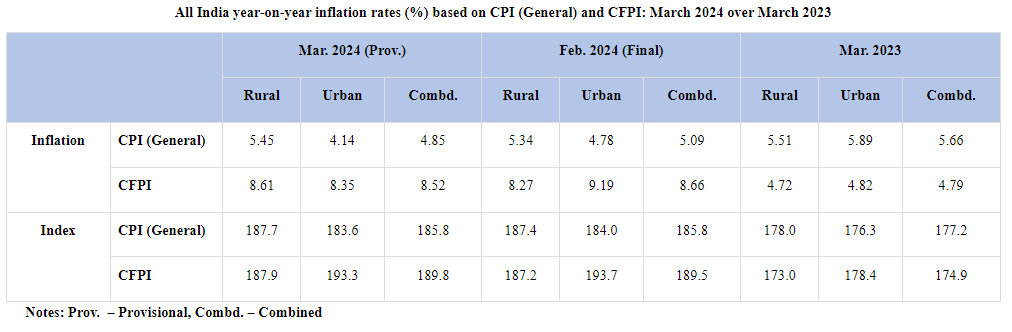
According to official data released on Friday, retail inflation dropped to its lowest in five months, standing at 4.85 percent in March, primarily attributed to reduced food prices.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) based retail inflation was 5.09 per cent in February and 5.66 per cent in March 2023. Previously, CPI-based inflation was the lowest at 4.87 per cent in October 2023.
The inflation in the food basket was at 8.52 per cent in March, down from 8.66 per cent in February, according to the data released by the National Statistical Office (NSO).
The government has tasked the Reserve Bank to ensure inflation remains at 4 per cent, with a margin of 2 per cent on either side.
According to the Reserve Bank, which factors in consumer inflation while arriving at its bi-monthly monetary policy, food price uncertainties continue to weigh on the inflation trajectory going forward. The central bank has projected retail inflation at 4.5 per cent for the current fiscal assuming a normal monsoon.
Continuing geopolitical tensions also pose an upside risk to commodity prices and supply chains.
The RBI projected inflation at 4.9 per cent in the April-June quarter and at 3.8 per cent for the September quarter.
(With PTI inputs)